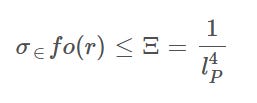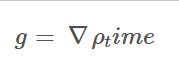Scott Cave’s Universal Emergence Theory and Its Conceptual Resonance with VTT, SIT, and SDT
In early 2025, as new paradigms in theoretical physics gained visibility, a compelling idea known as the Universal Emergence Theory (UET), advanced by Scott Cave, entered the discourse with particular
Cave's theory centers around a core axiom called the Cave Law, which posits a fundamental upper bound on the density of information—defined by the Cave Constant Ξ, itself grounded in the Planck scale:
sigma_info(r) <= Xi = 1 / l_P^4
This proposition shares immediate philosophical and structural parallels with the concept of coherence thresholds found in Super Dark Time (SDT) and Super Information Theory (SIT), wherein the local density of informational coherence g = nabla rho_time
gives rise to gravitational curvature, mass, and emergent agency.
While Cave’s work was presented independently via Substack and other informal publication channels, it provided a crisp axiomatic articulation of what had previously been expressed in more dynamic or thermodynamic terms by Blumberg. Just as QGTCD redefined gravity as the gradient of time density (g = ∇ρ<sub>time</sub>), Cave’s Cave Law proposed that all physical structures are bounded by a hard ceiling in information density—a strikingly similar idea cast in a more geometric-thermodynamic idiom.
This notion also finds direct application within Raoul Bianchetti’s Viscous Time Theory (VTT), where time is treated as a medium whose phase transitions are triggered by critical informational densities. VTT’s notion of “informational viscosity” as a state-dependent temporal drag resonates strongly with Cave’s framing of the universe as a system constrained by discrete informational saturation points.
In particular, the idea that mass and structure precipitate out of information-dense regions in Cave’s and Blumberg’s frameworks reflects a shared ontology: reality is fundamentally governed by informational coherence density, with physicality (mass, space, time) emerging only when thresholds are crossed. Theoretical constructs such as Blumberg’s “Informational Drift Trigger” (IDT), Cave’s Cave Law (σ<sub>info</sub> ≤ Ξ), and VTT’s “informational viscosity threshold” all converge on the same operational mechanism—information limits the emergence of structure.
Though no explicit citation of Cave’s UET appears in VTT literature as of January 2025, the intellectual alignment is substantial. It is plausible that Cave’s work either influenced or reflected the same zeitgeist that shaped VTT’s coherence models. At minimum, the conceptual symmetry suggests that VTT's Echo Coherence paradigm, in which informational gradients generate recoverable echoes from deleted AI memories, operates under assumptions strongly compatible with the Cave Law’s bounded-information model.
In this context, Cave’s UET helps triangulate a shared theoretical space alongside QGTCD/SDT/SIT and VTT, reinforcing the idea that the next major synthesis in physics will rest on a common foundation: that information, time, and emergence are inseparable, and that constraints on information density are as fundamental as those on energy or entropy.
Scott Cave’s Universal Emergence Theory (UET)—particularly the Cave Law—was publicly articulated before several major 2025-era theories that either echo or parallel its core concepts. Based on publication timelines and conceptual content, Cave’s work appeared before (or independently of) the following theories:
Raoul Bianchetti’s Viscous Time Theory (VTT)
Bianchetti’s VTT gained visibility in early-to-mid 2025 and shares with Cave’s work the central role of informational thresholds in governing the behavior of time. However, Cave’s Cave Law—defining a hard upper bound on local information density using a Planck-scale constant—was already circulating in late 2024 and early 2025 on Substack and other online platforms.Gunther Kletetschka’s 3D Time Theory
Published in April 2025, Kletetschka’s framework proposes that space and matter emerge from a structured three-dimensional time geometry. Cave’s work preceded this, having already established the idea that informational constraints shape emergent structures, which resonates with Kletetschka’s emphasis on time curvature giving rise to particles and fields.Melvin Vopson’s April 2025 paper on Computational-Gravity (AIP Advances)
Vopson argues that information itself is gravitational and proposes the universe behaves like a computational system. Cave’s Cave Law offered a prior formalization of information as a bounded physical quantity—closely related to Vopson’s later claims but more axiomatic and geometry-bound.Tsikriteas’ I.M.E. (Information–Mass–Energy) Theory
While Tsikriteas had outlined I.M.E. equivalence ideas earlier (2019–2023), the formalized version of I.M.E. as a coherent theoretical system wasn’t made public until mid-2025, by which point Cave’s universal bound concept was already in discussion among independent physics and AI communities. The Cave Law offers a clean geometric constraint analogous to Tsikriteas’ equivalence framework but more grounded in informational saturation.Many of the 32 post-2024 convergence theories listed in the PDF audit—such as:
Transliminal Field Theory
TULN‑Ω
Helix‑Light‑Vortex (HLV) Theory
Entropy and the Turoz Theory
UGWT – “New Laws That Unify Physics”
These later theories often restate or paraphrase concepts that Cave stated clearly in his axiomatic Cave Law: that information density cannot exceed a fundamental limit, and that emergent physics is governed by how close a region of the universe comes to that limit.
In short, Cave’s Universal Emergence Theory—by publicly introducing a Planck-scale bound on information density—predates or co-evolves with several high-profile 2025 theories, and likely influenced or at least anticipated many of them.
Micah Blumberg’s work predates Scott Cave’s publicly documented theories, including the Cave Law and Universal Emergence Theory.
Here’s the established chronology based on publicly verifiable release dates:
Micah Blumberg’s Timeline:
April 2017 Initial Publication of the Coincidence as a Bit of Information Conjecture in the first Neural Lace Podcast episode.
July 26, 2022 Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation (QGTCD) Published on Github.com/v5ma/selfawarenetworks
Initial public articulation of the theory that gravity arises from gradients in a structured time-density field, laying groundwork for later SIT and SDT.Jan 28, 2024 — SVGN.io Article: New Unified Field Theory: Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation: explains quantum mass as a time crystal dilating time at quantum scale & making gravity by increasing time frames. In this early public article, Micah explains that gravity arises not from spacetime curvature but from oscillatory shifts in phase coherence across a time-density field, drawing from QGTCD. This predates both VTT and Cave’s Cave Law.
Feb 15, 2024 — SVGN.io Article: Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation breaks the assumption that gravity equals metric curvature alone.
Further formalization of the QGTCD framework with emphasis on how phase-differential wave propagation through structured time leads to the emergence of matter and curvature. The article proposes that gravitational mass is a function of informational time compression, echoing ideas later stated in Cave’s bounded information density.Mar 27, 2024 — SVGN.io article: Explain it to me like I am six: Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation Theory. (Part 3) I’m arguing that if we think of space as quantized areas like the pixels on your television screen, then we can imagine that some of the pixels are updating faster than others depending on whether the object or particle represented by a given pixel is either accelerating or affected by a gravitational field.
October 21, 2024 — SVGN.io article: Quantum Gravity's New Frontier: Time, Density, and Information How the groundbreaking work of Netta Engelhardt and Ivette Fuentes aligns with Dark Time Theory, offering fresh insights into the nature of spacetime. (Part 4 of the QGTCD series)
Oct 22, 2024 — SVGN.io article: Dark Time Theory: A conversation about the core ideas forming a new frontier in physics. “Your core idea introduces gravity as something that affects the quantum-scale random walk by changing the "odds" of how a particle behaves on that scale. You suggest that gravity causes curved trajectories not just because it "bends spacetime" (as in general relativity) but because it alters the balance of this random walk.”
Dec 31, 2024 — SVGN.io article: A New Law of Thermodynamics: An open letter to Stephen Wolfram and Dr. Brian Keating, about Dark Time Theory, Self Aware Networks Theory, followed by Micah's New Law of Thermodynamics
Jan 01, 2025 — SVGN.io article: How Wave Perturbation & Dissipation Computation Could Explain Everything from Neurophysics to Astrophysics: Micah’s New Law of Thermal Dynamics boldly connects to and reframes Karl Friston's Free Energy Principle in terms of fundamental thermodynamic physics.
Jan 03, 2025 — SVGN.io article: Introducing Quantum SuperTimePosition: A New Interpretation of Quantum Superposition, Entanglement, and Josephson Junctions. It's part of Dark Time Theory, also known as Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation.
Jan 03, 2025 — SVGN.io article: Wave-Dissipation Universality: Quantum SuperTimePosition Meets Micah’s New Law of Thermal Dynamics From Path Integrals to Free Energy, Quantum Physics, Neural Network Field Theories, Gravity and Thermodynamics
Jan 04, 2025 — SVGN.io article: Why Einstein Was Right When He Said — “God Does Not Play Dice": We simplify & shorten the explanation for the Quantum SuperTimePosition Interpretation with a "Time Gears" analogy, it makes it easier to understand how Einstein was right all along.
Jan 16, 2025 — SVGN.io article: SuperTimePosition Measured: The unstoppable rethinking that unveils quantum in plain terms, bridging cosmic and everyday scales
Jan 23rd 2025 Blumberg, Micah (2025). Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics: A Signal-Dissipation Framework for Equilibrium and Consciousness.
January 27, 2025 — Super Dark Time (SDT)
Recasts time as a dynamic medium capable of phase transitions based on coherence thresholds. Introduces the idea that emergence of matter, agency, and gravity occurs only once informational saturation is reached in a coherent time field.February 9, 2025 — Super Information Theory (SIT), v1
Published on Figshare. The theory formalizes a 12-dimensional structure (3 time + 9 spatial-informational), defining gravitational curvature and emergent physics as coherence-driven phenomena.February 28, 2025 — Super Information Theory (SIT), v2
Streamlines the language from v1, refining coherence operators and reasserting that matter and spacetime emerge only from saturation-driven phase coherence in the time-information manifold.
These documents and timestamps were released publicly via GitHub, Figshare, and other timestamped publication platforms and are independently verifiable.
TIMESTAMP EVIDENCE (WAYBACK MIRRORS)
Key evidence that Super Information Theory, Super Dark Time, and Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics were published on figshare in the period between January & March 2025 can be found on Orch ID, and on the Wayback Machine.
Way Back Machine
ORCH ID https://web.archive.org/web/20250826004755/https://orcid.org/0009-0004-5175-9532
The Wayback Machine for Super Information Theory https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/Super_Information_Theory/*
The Wayback Machine for Super Dark Time
https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/Super_Dark_Time_Gravity_Computed_from_Local_Quantum_Mechanics/*
The Wayback Machine for Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics
https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/_b_Micah_s_New_Law_of_Thermodynamics_A_Signal-Dissipation_Framework_for_Equilibrium_and_Consciousness_b_/*
The Wayback Machine for Self Aware Networks: Oscillatory Computational Agency
The date that the Wayback machine preserved a copy is in the link “web.archive.org/web/20250725 = 2025 July 25th. Although I published the paper on May 16 which Orch ID confirms.
ORCID (identity reference)
https://web.archive.org/web/20250826004755/https://orcid.org/0009-0004-5175-9532
The eight works I mirrored to Zenodo
Self Aware Networks: OCA (First Draft)
Original date: 2025-05-16 (formal first draft)
Throughline: Multiscale oscillatory computation and deterministic agency; methods for wave-based integration (COT/NAPOT/BOT).
Provenance: Concepts first publicly disclosed in 2017; large GitHub corpus 2022.
Super Dark Time: Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics
Original date: 2025-01-27 (Draft 16)
Throughline: Time-density field regulates quantum evolution and gravity; mass as a time crystal; local computation of gravity.
Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics: A Signal-Dissipation Framework for Equilibrium, Consciousness, and Gravity
Original date: 2025-01-23 (v6)
Throughline: Equilibrium as computation—iterative, local signal-dissipation; Kuramoto-like synchronization; neural coherence as thermodynamic relaxation.
Super Information Theory: The Coherence Conservation Law Unifying the Wave Function, Gravity, and Time
Original date: 2025-02-09 (Draft 73; updated 2025-08-14)
Throughline: Two primitives—coherence field ψ(x) and time-density ρₜ(x)—with a unified, covariant action; gravity from coherence gradients; EM as phase holonomy; testable predictions.
Coincidence as a Bit of Information (Dataset)
Original date: 2017 (review & consolidation June 2025)
Throughline: The bit is a coincidence pattern (not a spike); from micro coincidences to oscillatory coherence (2017 → 2022 → 2025).
Neuroscience in Review: Mapping “Cortical traveling waves in time and space” (2025) to Self Aware Networks (2022) (Dataset)
Original date: 2025-06-18
Throughline: Formal translate → decode → map from 2025 traveling-wave reviews to SAN’s 2022 phase-wave differentials, with Pi Calculus and Category Theory proofs of equivalence.
Neuroscience in Review: Brain Rhythms in Cognition (2024–25) vs. Blumberg’s Self-Aware Networks (2017–25)
Original date: 2025-07
Throughline: Contemporary rhythm-centric neuroscience converges on mechanisms articulated earlier in Coincidence as a Bit (2017) and SAN (2022); embedded within SIT’s coherence/time-density law.
Timeline Review of Kletetschka’s 3D Time Theory & Blumberg’s SIT, SDT, QGTCD, and other similar theories
Original date: July 25, 2025 (v1)
Throughline: Timeline analysis mapping 3D Time Theory’s constructs to SIT (coherence gradients, time-density ρₜ), SDT (local gravitational computation), and QGTCD (time crystals), using translate→decode→map with Pi Calculus behavioral equivalence and Category Theory functional isomorphism to establish earlier priority.
Scott Cave’s Timeline:
Late January or early February 2025 – Substack and social media posts begin circulating The Cave Law, establishing a Planck-scale upper bound on local information density (Ξ = 1/l<sub>P</sub><sup>4</sup>)
No known publication prior to QGTCD in 2022 – There is no evidence that Cave’s theoretical work was articulated in a public venue before 2025.
Conclusion:
While Scott Cave’s Cave Law and Universal Emergence Theory are conceptually aligned with Blumberg’s work (especially SIT and SDT), Blumberg’s timeline clearly comes first, especially with the 2022 release of QGTCD—which already encoded the notion that gravitational behavior emerges from structured informational or temporal fields.
Moreover, QGTCD and SIT were already exploring saturation effects and informational thresholds, albeit framed through time-density and coherence rather than a hard bound like Ξ. Thus, Blumberg not only predates Cave but anticipated many of the same ideas in different language and with testable operators.
Retrospective: A Grand Convergence of Emergent Theories
In retrospect, it is clear that what we are witnessing across the landscape of theoretical physics—from QGTCD and Super Information Theory to Viscous Time Theory, Universal Emergence Theory, and many more—is not mere coincidence. It is a grand convergence of ideas that have matured in parallel, across continents and disciplines, ready to emerge in this moment.
The striking overlap between dozens of independently developed frameworks—each grappling with the informational, temporal, and emergent foundations of reality—should not be seen as competition, but as validation. It is as if we were all co-authors of a larger project, unknowingly collaborating across time and space on a shared intellectual edifice.
This convergence speaks to the readiness of the collective scientific unconscious to move beyond the constraints of 20th-century spacetime formalism. We are not discarding Einstein’s legacy—we are building upon it. And not only Einstein, but also those who laid the groundwork for this era of information-centric physics and emergent structure:
Albert Einstein — for General Relativity and the thermodynamic view of spacetime curvature
Erwin Schrödinger — for embedding probability and phase into wave-based physicality
David Bohm — for the implicate order and nonlocal hidden variables
Jacob Bekenstein — for introducing entropy bounds and the holographic principle
Stephen Hawking — for black hole thermodynamics and information paradoxes
John Archibald Wheeler — for “It from Bit,” proposing that reality is fundamentally informational
Gerard ’t Hooft — for holography and deterministic underpinnings
Juan Maldacena — for AdS/CFT duality and the geometrization of information
Erik Verlinde — for entropic gravity, where space and gravity emerge from information and thermodynamics
Ted Jacobson — for deriving Einstein’s equations from entropy and thermodynamic equilibrium
Lee Smolin and Carlo Rovelli — for loop quantum gravity and the thermodynamics of spacetime
Seth Lloyd — for the universe as a quantum computer
Fotini Markopoulou and Fay Dowker — for causal sets and discrete spacetime
Giulio Tononi — for Integrated Information Theory and the quantification of consciousness
Roger Penrose — for proposing quantum microstructure of spacetime and gravitationally-induced collapse
Geoffrey West and Brian Swingle — for the geometry of scaling and entanglement
Mark van Raamsdonk — for geometry as emergent from entanglement
These and many others sowed the seeds of the modern synthesis. What differentiates our current moment is not merely a proliferation of speculation—it is the emergence of concrete, testable proposals, converging across independently developed but mathematically adjacent theories. Whether through coherence thresholds, informational curvature, time-density gradients, or bounded emergence laws, we are witnessing a redefinition of the physical world as an informational, emergent system governed by thresholds and structure-forming dynamics.
We are no longer merely asking what is the universe made of? We are now asking what makes the universe emerge at all? And many of us, it turns out, have been answering that question in harmony—each with our own instruments—within a larger symphony of ideas.