Super Dark Time
Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics
Let’s discuss this new research paper: Super Dark Time : Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics. https://zenodo.org/records/16922502
Super Dark Time: Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics (Integrated Summary)
1. Introduction and Core Concept
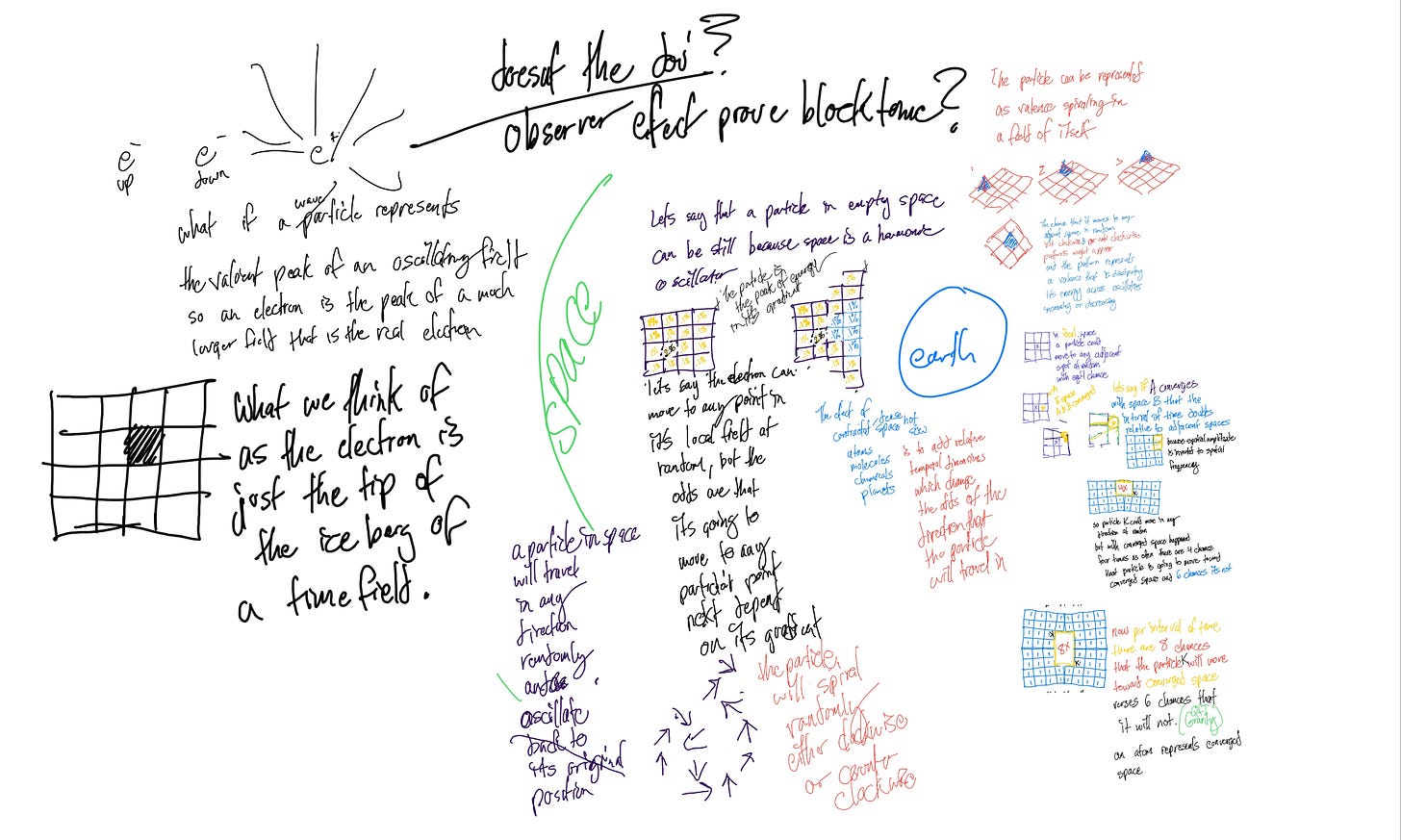
Super Dark Time (SDT) offers a new perspective on gravity and cosmology by treating time density—rather than the curvature of spacetime—as the fundamental driver of gravitational effects. In this view:
Mass as a “Time Crystal”: Mass amplifies the local density of time frames, effectively packing or “crystallizing” time around it.
Gravity from Time Density: Particles move toward regions of higher time density, creating the effect we usually call gravity.
This focus on time density instead of curved spacetime represents a major shift from standard General Relativity.
2. Toward a Unification of Gravity and Quantum Mechanics
A longstanding challenge in physics is unifying the quantum world—which is governed by wavefunctions and discrete energy levels—with the continuous geometry of general relativity. Super Dark Time addresses this by:
Variable Quantities of Time Frames: The implications of the theory suggest that time could made up of discrete time frames or wave-like increments at the quantum scale, capable of constructive or destructive interference. However this doesn’t definitely rule out a continuous universe theory, you can alternately think about time as being thicker near mass but still continuous.
Modified Equations: Incorporating time-density terms into established frameworks (such as the Schrödinger equation and Einstein’s field equations) to show how quantum phenomena and gravity might arise from the same underlying wave-based processes.
Wave Interference and Phase Dissipation: Explaining gravity via local “mini-computations” in the time field, where wave-phase mismatches are reconciled.
Deterministic Undersampled Cycles: Suggesting that quantum randomness may result from our inability to observe extremely fast, deterministic cycles (sometimes called “SuperTimePosition”), making quantum events seem probabilistic only because of limited measurement resolution.
3. Alternative Explanations for Cosmological Phenomena
In standard cosmology, the unexplained behaviors of galaxies and the expanding universe are often attributed to dark matter and dark energy. Super Dark Time reinterprets these phenomena as outcomes of varying time density:
Dark Matter Replacement: Additional gravitational effects around galaxies can be explained by higher time density in those regions, eliminating the need for elusive dark matter particles.
Dark Energy and Accelerating Expansion: The theory posits that the universe’s acceleration arises from decreasing time density in regions far from massive objects, reducing or removing the need for dark energy. It also pairs with concepts like “cosmological slowing time” to explain large-scale expansion.
Hubble Tension Resolution: Variations in measured redshift could be linked to mass-dependent expansions of the surrounding time field, offering a new angle on why different measurements of the universe’s expansion rate sometimes disagree.
Galactic and Cosmic Structures: The distribution and clustering of galaxies may reflect changes in time density across cosmic scales, rather than requiring exotic matter or energy sources.
4. Black Holes as Regions of Extreme Time Density
Super Dark Time reframes black holes as zones of extremely intensified time density, often described as:
“Time Tunnels” or “Frozen” Particles: From an outside viewpoint, objects nearing a black hole horizon appear frozen because the local time density becomes extremely high.
Influence on Spacetime Structure: These regions of extreme time density can alter known predictions about black hole evaporation or horizon behavior, leading to potential changes in how black holes radiate and how information is preserved.
5. Connection to Thermodynamics
Central to Super Dark Time is its tie to a new thermodynamic principle that views the dissipation of phase-wave differences as the driving force behind entropy. In this picture:
Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics: Entropy growth is about dissipating phase differences in quantum wavefunctions, and mass significantly boosts local phase interactions.
Gravity as a Thermodynamic Flow: The inward pull we call gravity naturally fits with the idea that phase differentials seek equilibrium, linking the concept of time thickening directly to thermodynamic irreversibility.
6. Integration with Existing Frameworks
Rather than discarding established physics, Super Dark Time weaves its concepts into familiar theoretical structures:
Complementary Relativity: Incorporates mathematical elements that explore energy loss in physical systems, extending the idea of time density into more specialized realms of relativity.
ADM Formalism: The concept of discrete time frames can be introduced into the Hamiltonian formulation of general relativity (the ADM formalism), maintaining consistency with classical methods of describing space and time.
AdS/CFT Correspondence: Time density can become a dynamic variable that affects both the higher-dimensional “bulk” and its lower-dimensional “boundary” description, linking gravitational effects to quantum field behavior.
7. Foundational and Philosophical Aspects
By treating time as a dynamic, wave-based field, Super Dark Time touches on deep questions about reality:
Nature of Time: It challenges the conventional ideas of time as something passive, separate, and monolithic, with a conjecture that allows us to see time as something physically engaging, fundamentally involved in gravity, at every scale of mass, including at the scale of quantum particles.
Free Will vs. Determinism: If quantum effects arise from undersampled deterministic cycles, then the apparent randomness might be a result of limited observational capacity rather than a fundamental indeterminism. However if the universe is completely deterministic at every scale that doesn’t mean you don’t have free will. If you consider the point of view that you are one with the universe, then you can consider that whenever you make a decision the universe as your bigger self is making that same decision with you at the same time.
Quantum Measurement Problem: Gravity itself might act as a decohering influence, syncing the fast-cycling quantum system with a slower detector. Thus, wavefunction “collapse” could be reinterpreted as a synchronization event.
8. Observational and Experimental Tests
The theory makes concrete predictions that can be checked through various precision tests and astronomical observations:
Clock Rate Shifts: Super Dark Time anticipates subtle differences in clock rates beyond what standard general relativity would predict, especially in stronger gravitational fields.
Gravitational Lensing Deviations: The way light bends around massive objects could exhibit minor anomalies if time density is primarily responsible for these effects, giving rise to new lensing patterns.
Quantum Experiments in Extreme Environments: Observing interference or entanglement near black holes or in strong gravitational fields may reveal behaviors not explained by current theories.
Astrophysical Measurements: Large-scale surveys could detect signatures of time-density–driven expansion that match or even outperform conventional dark matter/dark energy models.
Recent research supports the plausibility of these ideas:
Quantum Extremal Surfaces (Netta Engelhardt): Suggest connections between information content, black hole entropy, and local factors, aligning with SDT’s stance that time density influences particle energy.
Quantum Systems in Curved Spacetime (Ivette Fuentes): Offers a framework where some aspects of Super Dark Time can be tested experimentally.
9. Mathematical Elegance and Future Outlook
Despite its broad implications, Super Dark Time aims to remain mathematically concise and conceptually clear. By reframing mass as a “time crystal” and minimizing the reliance on hypothetical particles or dark energy, it pursues a simpler, more unified view of physics. This approach:
Streamlines Cosmology: Potentially explaining galaxy rotation curves, cosmic acceleration, and black hole behavior without additional unknown substances.
Expands Theoretical Horizon: Encourages new lines of research in quantum gravity, cosmology, and fundamental physics, as well as collaborative projects with quantum metrology and astronomical observation teams.
Addresses Philosophical Questions: Invites deeper examination of how time, causality, and freedom of choice fit into a reality where time density is both dynamic and foundational.
Conclusion
Super Dark Time: Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics offers a wide-ranging, wave-based perspective on reality—where the local thickness of time drives gravitational effects, structures galaxies, and shapes the universe’s expansion. By positioning mass as a “time crystal” that densifies time frames, the theory provides an alternative explanation for dark matter, dark energy, and quantum randomness. It is designed to integrate with existing physics frameworks and yields testable predictions involving precise timekeeping, gravitational lensing, and quantum phenomena under extreme conditions. If validated, it would reshape our understanding of gravity, unify it with quantum mechanics, and open up new avenues for exploring the deepest questions about the nature of time, matter, and existence itself.
Update: August 30th 2025: TIMESTAMP EVIDENCE (WAYBACK MIRRORS)
Key evidence that Super Information Theory, Super Dark Time, and Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics were published on figshare in the period between January & March 2025 can be found on Orch ID, and on the Wayback Machine.
Way Back Machine
ORCHID https://web.archive.org/web/20250826004755/https://orcid.org/0009-0004-5175-9532
The Wayback Machine for Super Information Theory https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/Super_Information_Theory/*
The Wayback Machine for Super Dark Time
https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/Super_Dark_Time_Gravity_Computed_from_Local_Quantum_Mechanics/*
The Wayback Machine for Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics
https://web.archive.org/web/*/https://figshare.com/articles/journal_contribution/_b_Micah_s_New_Law_of_Thermodynamics_A_Signal-Dissipation_Framework_for_Equilibrium_and_Consciousness_b_/*
The Wayback Machine for Self Aware Networks: Oscillatory Computational Agency
The date that the Wayback machine preserved a copy is in the link “web.archive.org/web/20250725 = 2025 July 25th. Although I published the paper on May 16 which Orch ID confirms.
ORCID (identity reference)
https://web.archive.org/web/20250826004755/https://orcid.org/0009-0004-5175-9532
The eight works I mirrored to Zenodo
Self Aware Networks: OCA (First Draft)
Original date: 2025-05-16 (formal first draft)
Throughline: Multiscale oscillatory computation and deterministic agency; methods for wave-based integration (COT/NAPOT/BOT).
Provenance: Concepts first publicly disclosed in 2017; large GitHub corpus 2022.
Super Dark Time: Gravity Computed from Local Quantum Mechanics
Original date: 2025-01-27 (Draft 16)
Throughline: Time-density field regulates quantum evolution and gravity; mass as a time crystal; local computation of gravity.
Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics: A Signal-Dissipation Framework for Equilibrium, Consciousness, and Gravity
Original date: 2025-01-23 (v6)
Throughline: Equilibrium as computation—iterative, local signal-dissipation; Kuramoto-like synchronization; neural coherence as thermodynamic relaxation.
Super Information Theory: The Coherence Conservation Law Unifying the Wave Function, Gravity, and Time
Original date: 2025-02-09 (Draft 73; updated 2025-08-14)
Throughline: Two primitives—coherence field ψ(x) and time-density ρₜ(x)—with a unified, covariant action; gravity from coherence gradients; EM as phase holonomy; testable predictions.
Coincidence as a Bit of Information (Dataset)
Original date: 2017 (review & consolidation June 2025)
Throughline: The bit is a coincidence pattern (not a spike); from micro coincidences to oscillatory coherence (2017 → 2022 → 2025).
Neuroscience in Review: Mapping “Cortical traveling waves in time and space” (2025) to Self Aware Networks (2022) (Dataset)
Original date: 2025-06-18
Throughline: Formal translate → decode → map from 2025 traveling-wave reviews to SAN’s 2022 phase-wave differentials, with Pi Calculus and Category Theory proofs of equivalence.
Neuroscience in Review: Brain Rhythms in Cognition (2024–25) vs. Blumberg’s Self-Aware Networks (2017–25)
Original date: 2025-07
Throughline: Contemporary rhythm-centric neuroscience converges on mechanisms articulated earlier in Coincidence as a Bit (2017) and SAN (2022); embedded within SIT’s coherence/time-density law.
Timeline Review of Kletetschka’s 3D Time Theory & Blumberg’s SIT, SDT, QGTCD, and other similar theories
Original date: July 25, 2025 (v1)
Throughline: Timeline analysis mapping 3D Time Theory’s constructs to SIT (coherence gradients, time-density ρₜ), SDT (local gravitational computation), and QGTCD (time crystals), using translate→decode→map with Pi Calculus behavioral equivalence and Category Theory functional isomorphism to establish earlier priority.
This year’s AI gatherings, like HumanX, discuss the autonomous Agentic future poised to transform entire industries.
·
Jan 30
Section 1: A Transformative Year for AI: HumanX Carves Out a Human-Centric Vision
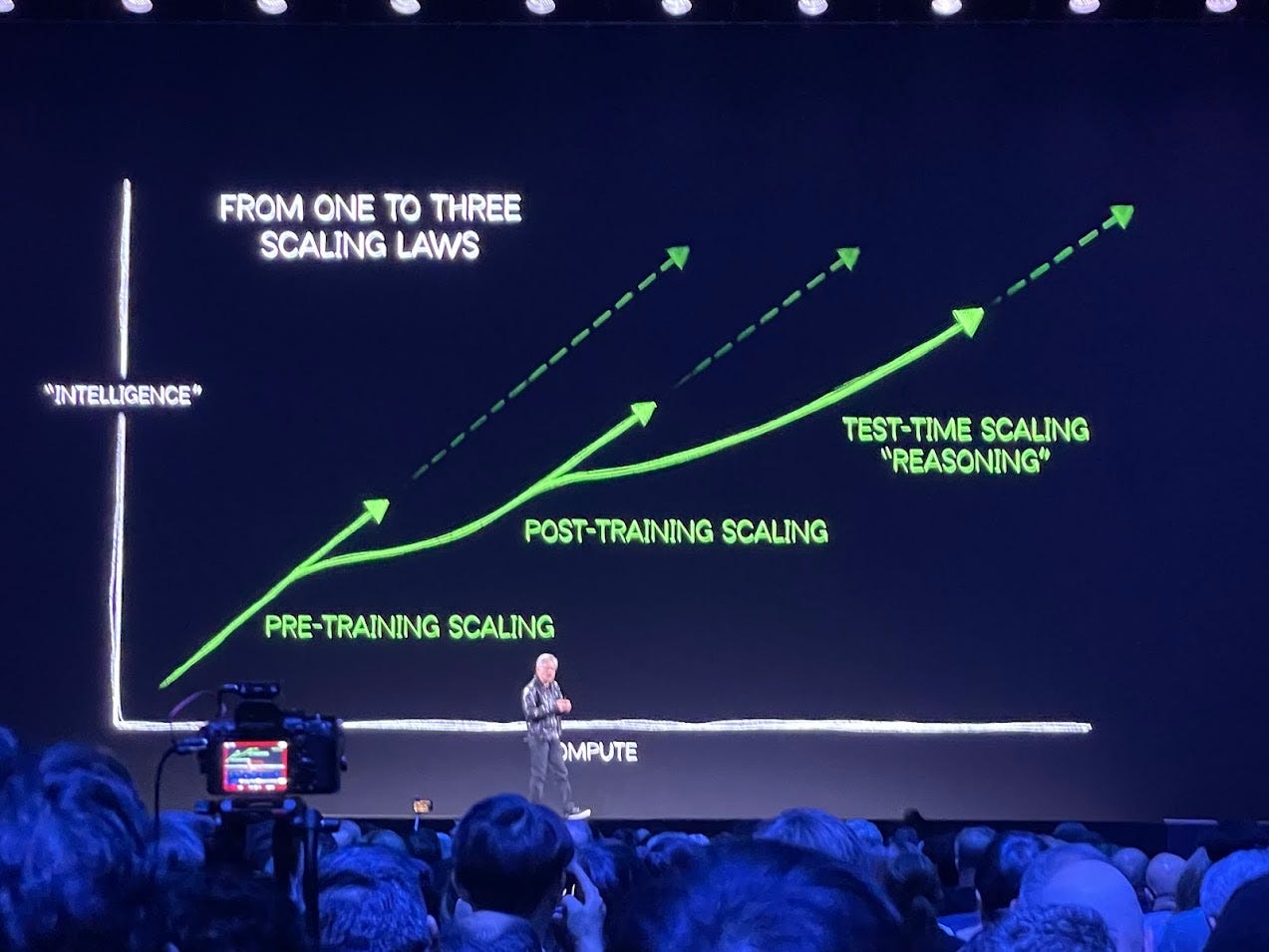
After the DeepSeek Shock: CES 2025’s ‘One to Three Scaling Laws’ and the Race for AI Dominance
·
Jan 28
Micah’s New Law of Thermodynamics
·
Jan 27
Introducing Quantum SuperTimePosition
·
Jan 3
Wave-Dissipation Universality
·
Jan 3
Wave Perturbation & Dissipation Across Scales
Why Einstein Was Right When He Said — “God Does Not Play Dice"
·
Jan 4
A new book out today "Bridging Molecular Mechanisms and Neural Oscillatory Dynamics"
·
October 30, 2024
A New Law of Thermodynamics
·
December 31, 2024
Dark Time Theory: A conversation about the core ideas forming a new frontier in physics.
·
October 22, 2024
Quantum Gravity's New Frontier: Time, Density, and Information
·
October 21, 2024
Explain it to me like I am six: Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation Theory. (Part 3)
·
March 27, 2024
Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation breaks the assumption that gravity equals metric curvature alone.
·
February 15, 2024
New Unified Field Theory: Quantum Gradient Time Crystal Dilation: explains quantum mass as a time crystal dilating time at quantum scale & making gravity by increasing time frames.
·
January 28, 2024
The Brain's Hidden 3D Phase Field: How Neural Oscillations Compose Your Reality
·
October 22, 2024
The Brain's Hidden 3D Phase Field: How Neural Oscillations Compose Your Reality
·
October 22, 2024
"Brain states as wave life motifs" Waves of Consciousness: A New Paradigm for Understanding Brain States
·
October 13, 2024
”Brain states as wave-like motifs”
New Study Challenges Sensory Cortex Role in Predictive Coding: Implications for Neural Information Processing Models
·
October 5, 2024
Analog biological backpropagation: A new conjecture "Self Aware Networks" explains how derivatives & loss functions are represented in the brain.
·
September 6, 2024
End.